×
![]()
Design Patterns are from the book:
- Gamma, E., Helm, R., Johnson, R. & Vlissides, J. Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented Software (1994) Addison-Wesley
Some references are from the book:
- Kuchana, P. Software Architecture Design Patterns in Java (2004) Auerbach
Note:
The term interface means application programming interface (API), unless stated otherwise.
| Purpose | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Creational | Structural | Behavioral | ||
| Scope | Class | |||
| Object | ||||
|
Factory Method
(class, creational)
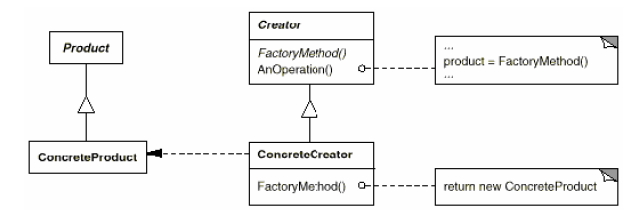
|
Intent
|
Example(s)
|
Advantage(s)
|
Disadvantage(s)
|
| Top | ||||
|
Abstract Factory
(object, creational)
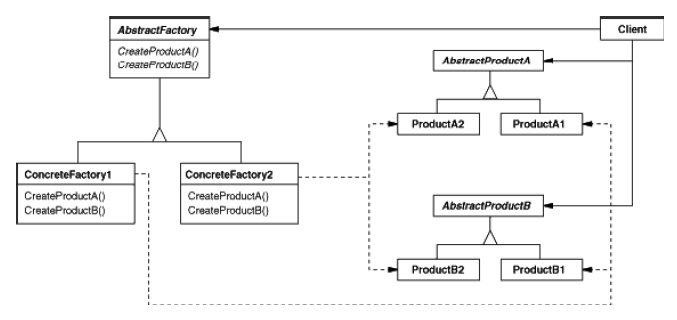
|
Intent
|
Example(s)
|
Advantage(s)
|
Disadvantage(s)
|
| Top | ||||
|
Builder
(object, creational)
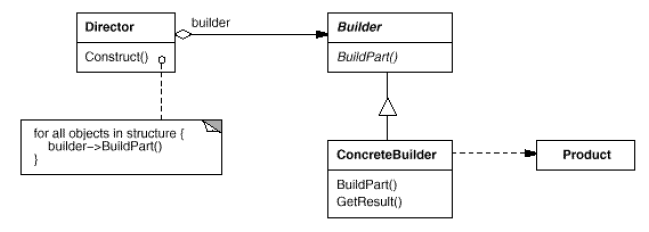
|
Intent
|
Example(s)
|
Advantage(s)
|
Disadvantage(s)
|
| Top | ||||
|
Prototype
(object, creational)
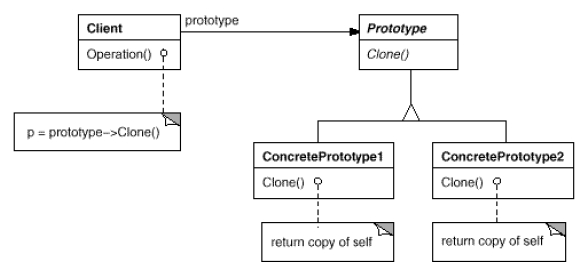
|
Intent
|
Example(s)
|
Advantage(s)
|
Disadvantage(s)
|
| Top | ||||
|
Singleton
(object, creational)
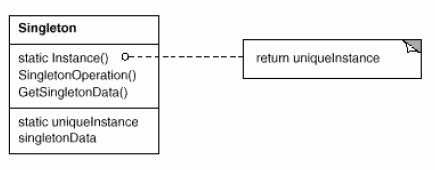
Implement with (synchronized) private constructor
|
Intent
|
Example(s)
|
Advantage(s)
|
Disadvantage(s)
|
| Top | ||||
|
Adapter
(class/object, structural)
Class adapter
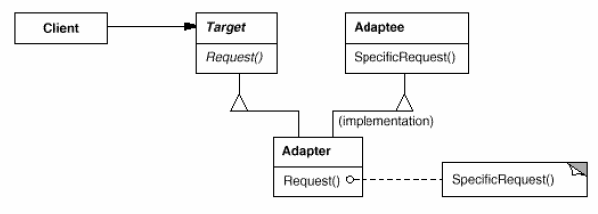
Object adapter
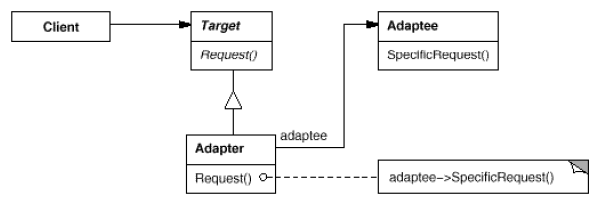 Class vs Object Adapters
Class vs Object Adapters
|
Intent
|
Example(s)
|
Advantage(s)
Class adapter
Object adapter
|
Disadvantage(s)
Class adapter
Object adapter
|
| Top | ||||
|
Bridge
(object, structural)
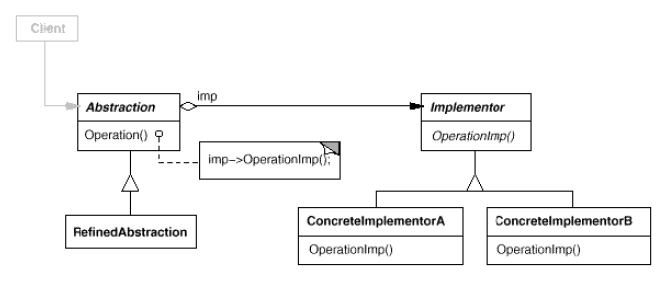
|
Intent
|
Example(s)
|
Advantage(s)
|
Disadvantage(s)
|
| Top | ||||
|
Composite
(object, structural)
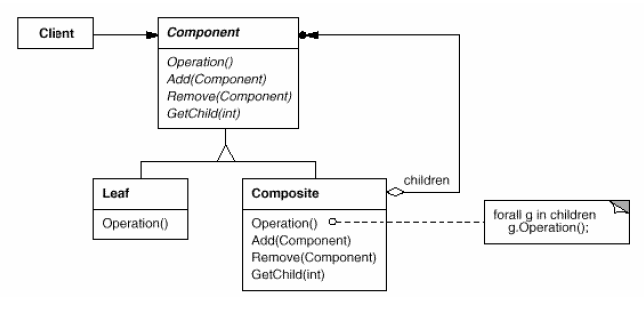
|
Intent
|
Example(s)
|
Advantage(s)
|
Disadvantage(s)
|
| Top | ||||
|
Decorator
(object, structural)
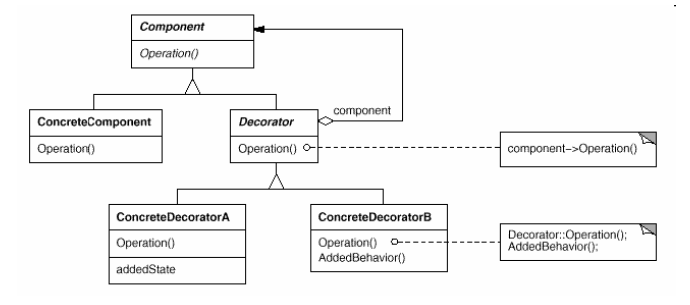
|
Intent
|
Example(s)
|
Advantage(s)
|
Disadvantage(s)
|
| Top | ||||
|
Façade
(object, structural)
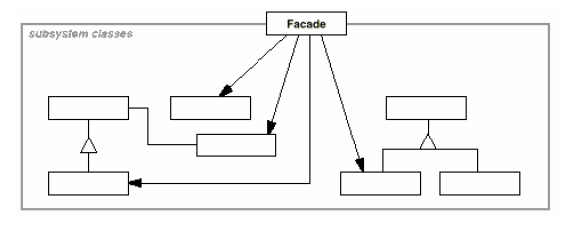
|
Intent
|
Example(s)
|
Advantage(s)
|
Disadvantage(s)
|
| Top | ||||
|
Flyweight
(object, structural)
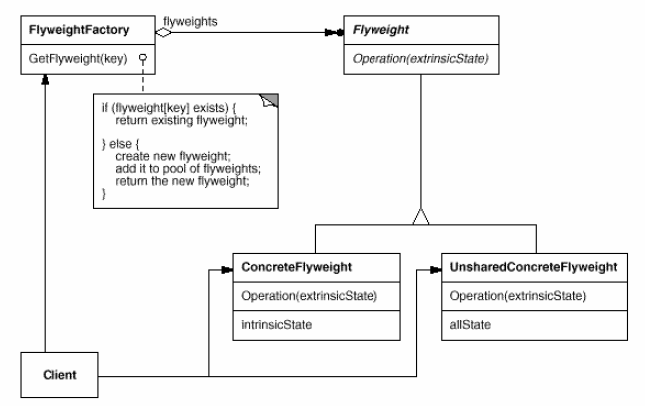
FlyweightFactory is a singleton
|
Intent
|
Example(s)
|
Advantage(s)
|
Disadvantage(s)
|
| Top | ||||
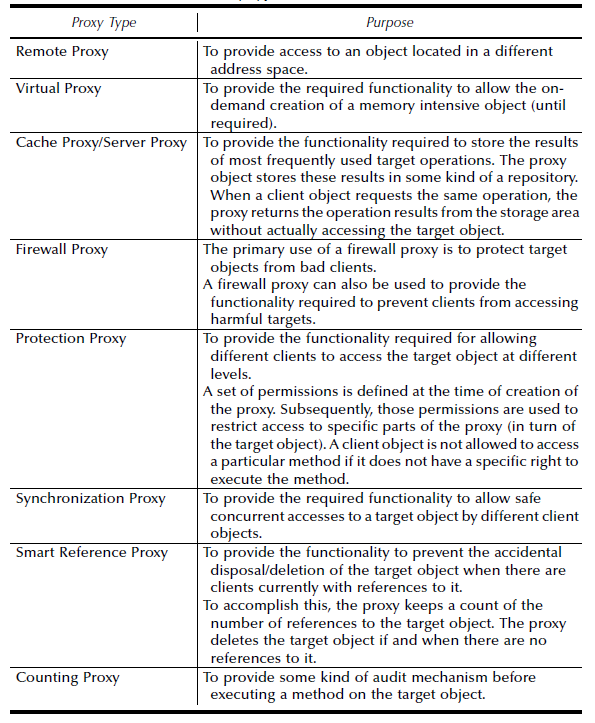
|
Proxy
(object, structural)
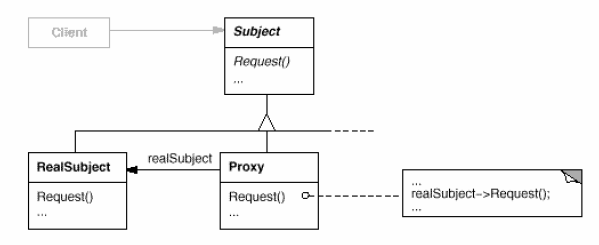
|
Intent
|
Example(s)
|
Advantage(s)
|
Disadvantage(s)
|
| Top | ||||
|
Interpreter
(class, behavioral)
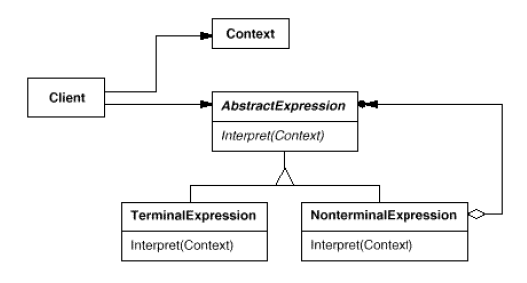
|
Intent
|
Example(s)
|
Advantage(s)
|
Disadvantage(s)
|
| Top | ||||
|
Template Method
(class, behavioral)
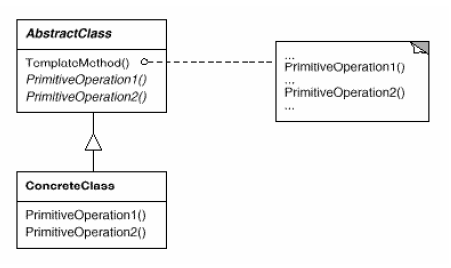
|
Intent
|
Example(s)
|
Advantage(s)
|
Disadvantage(s)
|
| Top | ||||
|
Chain of Responsibility
(object, behavioral)
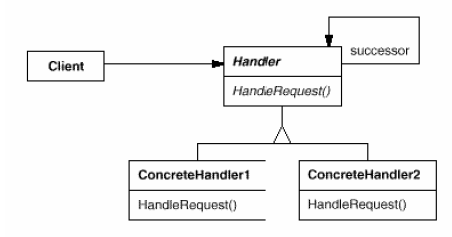
|
Intent
|
Example(s)
|
Advantage(s)
|
Disadvantage(s)
|
| Top | ||||
|
Command
(object, behavioral)
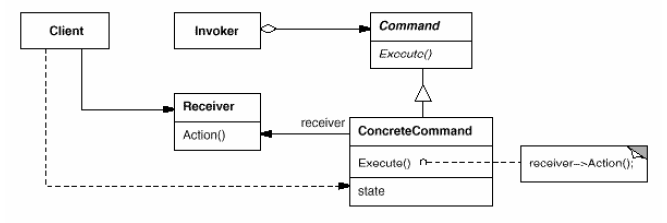
|
Intent
|
Example(s)
|
Advantage(s)
|
Disadvantage(s)
|
| Top | ||||
|
Iterator
(object, behavioral)
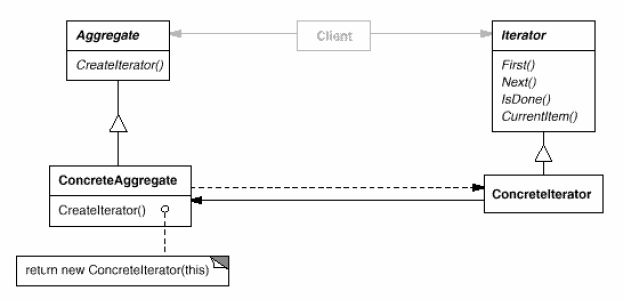
Can be internal or external
|
Intent
|
Example(s)
|
Advantage(s)
|
Disadvantage(s)
|
| Top | ||||
|
Mediator
(object, behavioral)
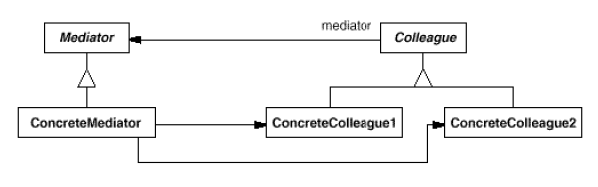
|
Intent
|
Example(s)
|
Advantage(s)
|
Disadvantage(s)
|
| Top | ||||
|
Memento
(object, behavioral)
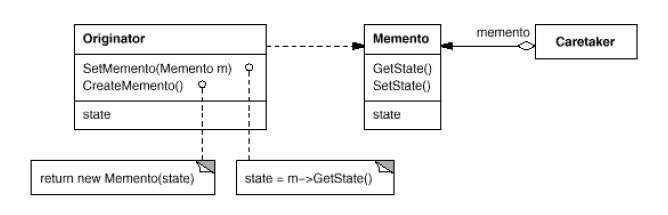
|
Intent
|
Example(s)
|
Advantage(s)
|
Disadvantage(s)
|
| Top | ||||
|
Observer
(object, behavioral)
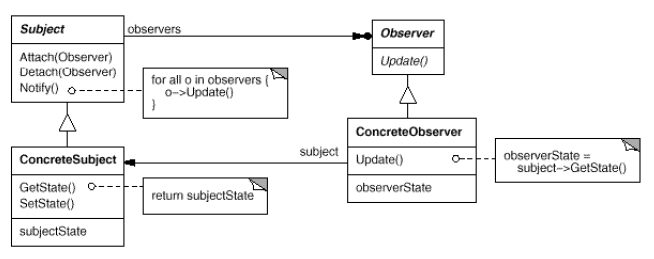
|
Intent
|
Example(s)
|
Advantage(s)
|
Disadvantage(s)
|
| Top | ||||
|
State
(object, behavioral)
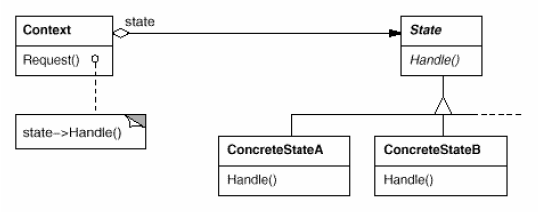
|
Intent
|
Example(s)
|
Advantage(s)
|
Disadvantage(s)
|
| Top | ||||
|
Strategy
(object, behavioral)
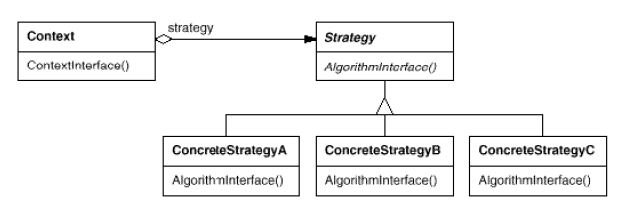
|
Intent
|
Example(s)
|
Advantage(s)
|
Disadvantage(s)
|
| Top | ||||
|
Visitor
(object, behavioral)
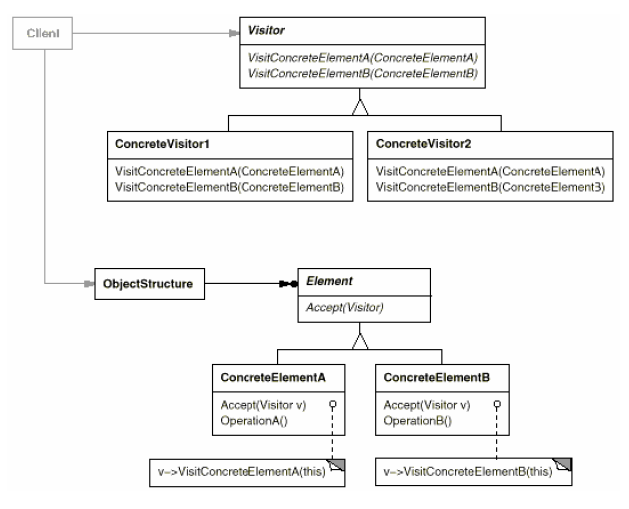
|
Intent
|
Example(s)
|
Advantage(s)
|
Disadvantage(s)
|
| Top | ||||
Shallow Copy vs Deep Copy
| Shallow Copy | Deep Copy |
|---|---|
| Original top-level object and all of its primitive members are duplicated | Original top-level object and all of its primitive members are duplicated |
| Any lower-level objects that the top-level object contains are not duplicated (only references to these objects are copied) | Any lower-level objects that the top-level object contains are also duplicated |
Result in original object and cloned object refer to same copy of lower-level object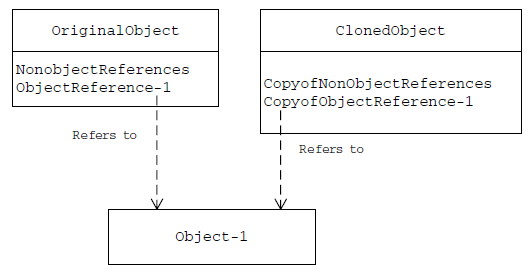 |
Result in original object and cloned object refer to different copy of lower-level object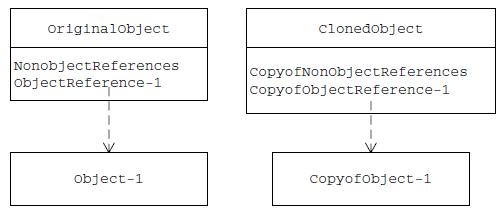 |
Class vs Object Adapters
| Class Adapters | Object Adapters |
|---|---|
| Based on the concept of inheritance | Use object composition |
| Can override some of the adaptee's methods | Cannot override adaptee's methods |
| Can be used to adapt the interface of the adaptee only but cannot adapt the interfaces of its subclasses because the adapter is statically linked with the adaptee when it is created | Can be used to adapt the interface of the adaptee and all of its subclasses |
| The client will have some knowledge of the adaptee's interface as the full public interface of the adaptee is visible to the client | The client and the adaptee are completely decoupled; only the adapter is aware of the adaptee's interface |
Internal vs External Iterators
| Internal Iterators | External Iterators |
|---|---|
| Iteration functionality (methods such as next, hasNext) is within the collection | Iteration functionality (methods such as next, hasNext) is separated from the collection; collection usually returns an appropriate iterator to the client |
| Only one iterator on a given collection at any given time | Multiple iterators on a given collection at any given time |
| Collection needs to maintain or save the state of iteration | Collection does not need to maintain or save the state of iteration |